PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
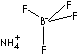
2826.90.9000
TOXICITY
SMILES
[B+3]([F-])([F-])([F-])[F-].[NH4+]
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white crystals
Decomposes
1.85
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Fluoroboric acid
Google Scholar Search - Ammonium Fluoroborate
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Ammonium Fluoroborate
PubChem Compound Summary - Ammonium Fluoroborate
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Ammonium Fluoroborate
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Ammonium Fluoroborate
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Ammonium Fluoroborate
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Ammonium Fluoroborate
Local:
Fluoroboric acid is used in plating circuits; metal finishing;
electropolishing of aluminium
and its alloy; component of galvanic baths; organic synthesis as catalyst for
alkylations and polymerisation; stabilisation of diazo salts; manufacturing of
inorganic fluoroborate salts.
Inorganic fluoroborate salts are used as components of fluxing and plating, as catalysts, in flame-retardant manufacture, in metal treatment; grain refining agents; as active fillers in resin bonded abrasives; in electrolytic generation of boron, preparation of glazing frits.
APPEARANCE
white crystals
97.0% min
PO4
0.02% max
SO4
0.15% max
SiO2
0.02% max
Cl
0.01% max
HEAVY METAL
10ppm max
50kg in bag
Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-36
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BORIC ACID
PRICE INFORMATION